
Gasoline Direct Injection Engine

I. Introduction
II.Major Objectives of the GDI engine
1.The difference between new GDI and current MPI
2.Outline
3.Technical features
III. Major characteristics of the GDI engine
1.Lower fuel consumption and higher output
2.Realization of lower fuel consumption
3.Realization of Superior Output

II. Major Objectives of the GDI engine

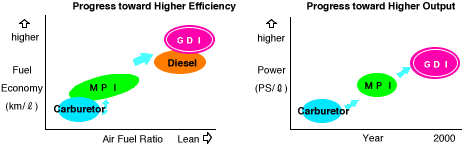
- Ultra-low fuel consumption that betters that of even diesel engines
- Superior power to conventional MPI engines
1. The difference between new GDI and current MPI
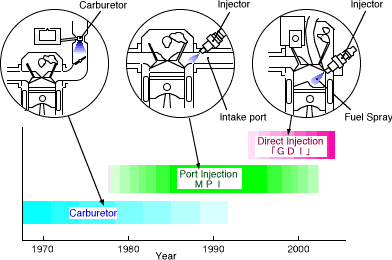
For fuel supply, conventional engines use a fuel injection system, which replaced the carburation system. MPI or Multi-Point Injection, where the fuel is injected to each intake port, is currently the one of the most widely used systems. However, even in MPI engines there are limits to fuel supply response and the combustion control because the fuel mixes with air before entering the cylinder. Mitsubishi set out to push those limits by developing an engine where gasoline is directly injected into the cylinder as in a diesel engine, and moreover, where injection timings are precisely controlled to match load conditions. The GDI engine achieved the following outstanding characteristics.
- Extremely precise control of fuel supply to achieve fuel efficiency that exceeds that of diesel engines by enabling combustion of an ultra-lean mixture supply.
- Very efficient intake and relatively high compression ratio unique to the GDI engine deliver both high performance and response that surpasses those of conventional MPI engines.
For Mitsubishi, the technology realized for this GDI engine will form the cornerstone of the next generation of high efficiency engines and, in its view, the technology will continue to develop in this direction.
Transition of Fuel Supply System
PREV
 NEXT
NEXT

 Copyright 1996 by Mitsubishi Motors Corporation.
Copyright 1996 by Mitsubishi Motors Corporation.


![]()

